What is Electrospinning? A Beginner’s Guide to the Technology Transforming Material Science and Drug Delivery
The Innovation Behind Electrospinning
Tom Freston once said, “Innovation is taking two things that already exist and putting them together in a new way.” This perfectly captures the essence of electrospinning — a ground-breaking technology that combines electricity and liquid polymers to create ultra-fine fibers. This technique is transforming industries such as medicine, textiles, energy, and even space technology.
From wound healing to high-performance filtration, electrospinning is at the heart of cutting-edge advancements. But where did it all begin?
A Brief History of Electrospinning
Although electrospinning gained significant attention in the 1990s due to breakthroughs in nano-sized fiber production, its origins go back over a century. The process was first patented by John Francis Cooley and W.J. Morton in the early 1900s. However, it was Anton Formhals in the 1930s who truly refined the technique, developing a mathematical model and optimised method for using electrical forces to produce polymer fibers.
Fast forward to today, and electrospinning has become an indispensable tool in material science, influencing research and commercial applications worldwide.
Understanding Electrospinning: How Does It Work?
Electrospinning is a fiber production technique that utilises electrical forces to draw polymer solutions or melts into ultra-thin fibers. The process involves five key steps:
- Polymer Solution Preparation — A polymer is dissolved in a suitable solvent to create a solution with the right viscosity and conductivity.
- High-Voltage Application — The polymer solution is loaded into a syringe, while a high-voltage power supply generates an electric field at the tip of the nozzle.
- Taylor Cone Formation — The electrical forces overcome the surface tension of the polymer droplet at the nozzle tip, forming a cone-like structure known as a Taylor cone.
- Fiber Jet Ejection — A thin fiber jet is ejected and undergoes stretching, elongation, and solvent evaporation before reaching a grounded collector.
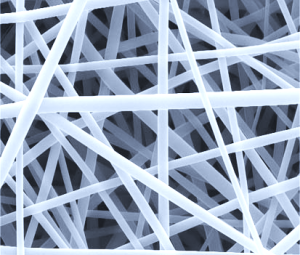
- Formation of Nanofibers — The collected fibers form a nonwoven mat with high porosity and a large surface-area-to-volume ratio, ideal for advanced material applications.
Applications of Electrospinning
Electrospinning is revolutionising various industries due to the versatility and functionality of its nanofibers. Some of its key applications include:
- Biomedical Engineering — Electrospun fibers are used in tissue engineering, wound dressings, and drug delivery systems due to their biocompatibility and controlled release properties.
- Filtration — The high surface-area-to-volume ratio makes these fibers ideal for air and liquid filtration, removing contaminants with high efficiency.
- Energy Storage — Nanofibers play a crucial role in battery separators and supercapacitors, improving energy efficiency and durability.
- Textile Industry — Electrospun fibers are used in smart textiles, protective clothing, and water-repellent fabrics, enhancing durability and functionality.
- Environmental Applications — These fibers aid in water purification, oil spill clean-up, and pollution control due to their exceptional absorption properties.
Advantages of Electrospinning
Electrospinning has gained popularity in material fabrication due to several advantages:
- Scalability — Suitable for both small-scale research and large-scale industrial production.
- Customisability — Enables precise control over fiber diameter, composition, and surface properties.
- High Surface Area — Provides enhanced mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties.
- Cost-Effectiveness — Requires relatively simple and affordable equipment compared to alternative nanofiber production methods.
Why Choose Electrospinning?
Unlike conventional fiber production techniques, electrospinning offers:
- Precision Control — Ability to manipulate fiber size and properties for specific applications.
- Versatility — Used across a wide range of industries, from medical research to aerospace technology.
- Scalability — Adaptable for both lab research and mass production.
The Future of Electrospinning
Electrospinning is a game-changer in material science, offering unmatched possibilities in nanofiber production. Whether you’re in biomedical engineering and drug delivery research, energy storage, textile innovation, or environmental sustainability, electrospinning presents a versatile and scalable solution for developing advanced materials.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of electrospinning are limitless. If you’re looking to integrate electrospinning into your research or industry, now is the time to explore its full potential!
Want to Learn More?
Genvolt is a global leader in high-voltage power supplies and electrospinning equipment, providing precision-driven solutions for research and industrial applications. Our cutting-edge technology supports advancements in electrospinning, electrospraying, pharmaceutical research, and beyond.
Committed to scientific progress, we collaborate with universities and industries, offering reliable equipment and expert guidance. Whether for nanofiber production, biomedical engineering, or other related research, Genvolt empowers researchers with high-performance solutions to drive innovation forward.
Contact us today to find out how our advanced electrospinning solutions can help you achieve ground-breaking innovations!